Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
<div id="mp-itn" style="padding:0.0em 0.5em;"> | <div id="mp-itn" style="padding:0.0em 0.5em;"> | ||
| − | <slideshow sequence="random" transition="fade" refresh=" | + | <slideshow sequence="random" transition="fade" refresh="5000"> |
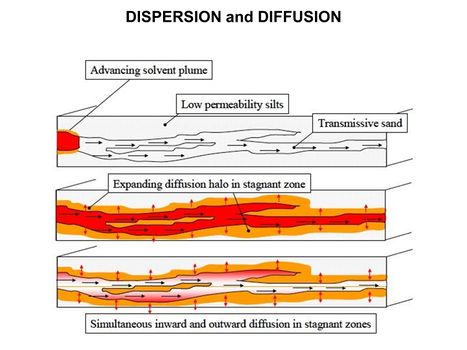
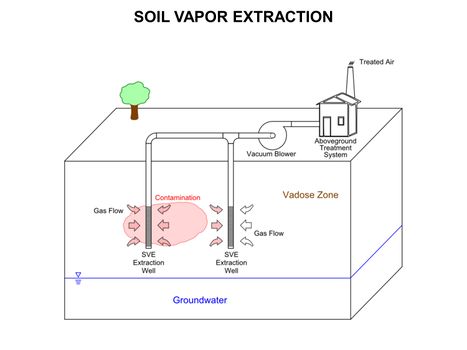
[[File:WH Picture1.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Dispersion and Diffusion|Molecular diffusion slowly transports solutes into clay-rich, lower permeability zones]] | [[File:WH Picture1.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Dispersion and Diffusion|Molecular diffusion slowly transports solutes into clay-rich, lower permeability zones]] | ||
| Line 75: | Line 75: | ||
*[[Dispersion and Diffusion]] | *[[Dispersion and Diffusion]] | ||
*[[Metals and Metalloids - Mobility in Groundwater | Mobility of Metals and Metalloids]] | *[[Metals and Metalloids - Mobility in Groundwater | Mobility of Metals and Metalloids]] | ||
| − | |||
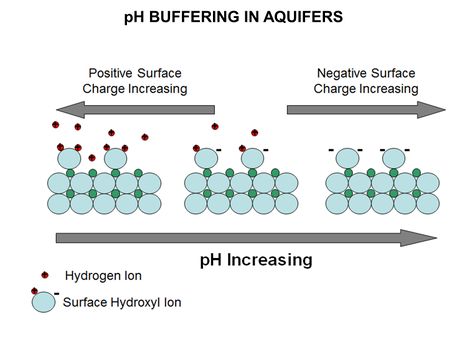
*[[pH Buffering in Aquifers]] | *[[pH Buffering in Aquifers]] | ||
*[[Sorption of Organic Contaminants]] | *[[Sorption of Organic Contaminants]] | ||
| Line 92: | Line 91: | ||
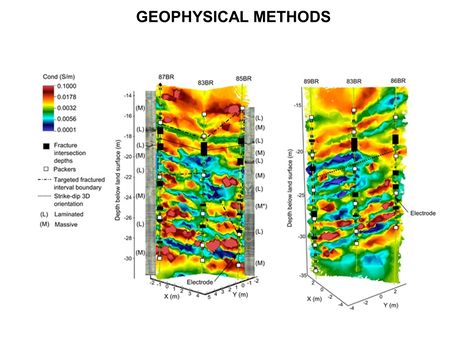
**[[Geophysical Methods - Case Studies | Case Studies]] | **[[Geophysical Methods - Case Studies | Case Studies]] | ||
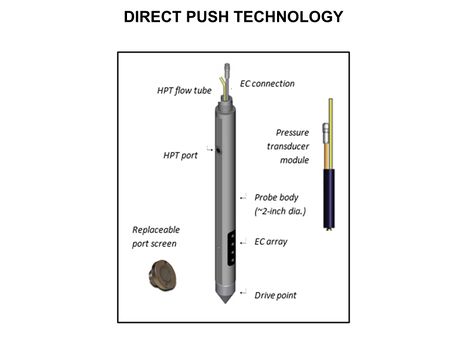
*[[Groundwater Sampling - No-Purge/Passive]] | *[[Groundwater Sampling - No-Purge/Passive]] | ||
| − | |||
*[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)|Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)]] | *[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)|Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)]] | ||
**[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Analysis | LTM Data Analysis]] | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Analysis | LTM Data Analysis]] | ||
| Line 114: | Line 112: | ||
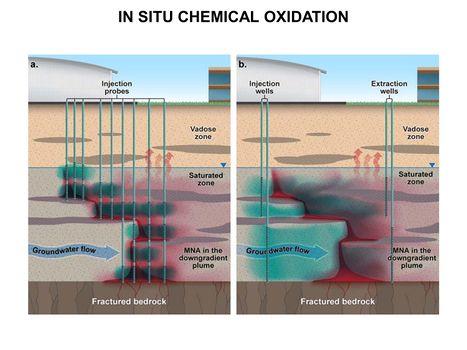
*[[In Situ Treatment of Contaminated Sediments with Activated Carbon]] | *[[In Situ Treatment of Contaminated Sediments with Activated Carbon]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>'''[[Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids (LNAPLs)]]'''</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[LNAPL Conceptual Site Models]] | ||
| + | *[[LNAPL Remediation Technologies]] | ||
| + | *[[NAPL Mobility]] | ||
<u>'''[[Munitions Constituents]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Munitions Constituents]]'''</u> | ||
| Line 163: | Line 167: | ||
*[[Injection Techniques - Viscosity Modification]] | *[[Injection Techniques - Viscosity Modification]] | ||
*[[Landfarming]] | *[[Landfarming]] | ||
| − | |||
*[[Metal and Metalloids - Remediation | Remediation of Metals and Metalloids]] | *[[Metal and Metalloids - Remediation | Remediation of Metals and Metalloids]] | ||
*[[Remediation Performance Assessment at Chlorinated Solvent Sites]] | *[[Remediation Performance Assessment at Chlorinated Solvent Sites]] | ||
| Line 183: | Line 186: | ||
*[[N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA)]] | *[[N-nitrosodimethylamine (NDMA)]] | ||
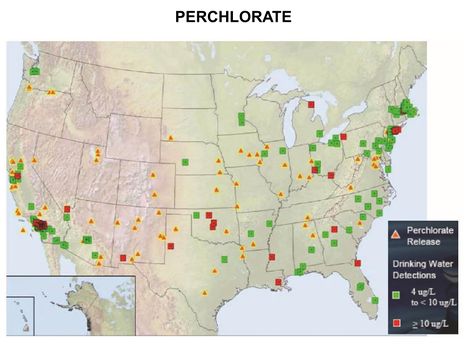
*[[Perchlorate|Perchlorate]] | *[[Perchlorate|Perchlorate]] | ||
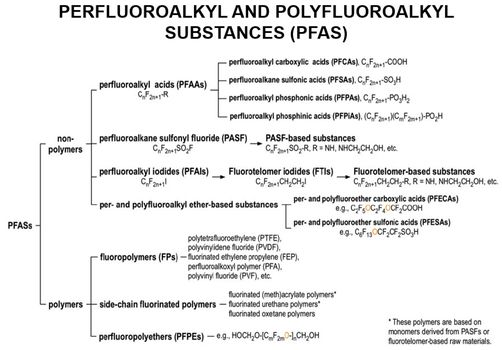
| − | *[[Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) | + | *[[Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)]] |
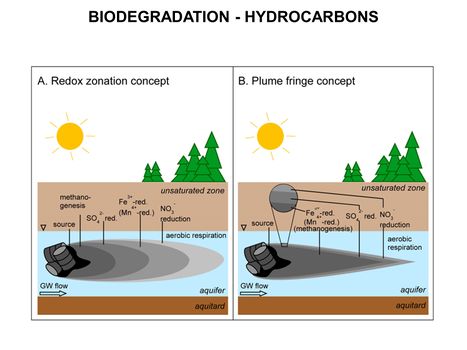
*[[Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHCs)]] | *[[Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHCs)]] | ||
*[[Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)]] | *[[Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)]] | ||
Revision as of 15:01, 17 September 2020
Peer Reviewed. Accessible. Written By Experts |
Your Environmental Information Gateway |
| The goal of ENVIRO.wiki is to make scientific and engineering research results more accessible to environmental professionals, facilitating the permitting, design and implementation of environmental projects. Articles are written and edited by invited experts (see Contributors) to summarize current knowledge for the target audience on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. | See Table of Contents |
Featured article: Sustainable RemediationThe ultraviolet (UV)/sulfite based reductive defluorination process has emerged as an effective and practical option for generating hydrated electrons (eaq- ) which can destroy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water. A UV/sulfite treatment system has been demonstrated in two field demonstrations in which it achieved near-complete defluorination and greater than 99% destruction of 40 PFAS analytes measured by EPA method 1633. Hydrated electrons can be produced by photoirradiation of solutes, including sulfite, iodide, dithionite, and ferrocyanide, and have been reported in literature to effectively decompose per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water. The hydrated electron is one of the most reactive reducing species, with a standard reduction potential of about −2.9 volts. Though short-lived, hydrated electrons react rapidly with many species having more positive reduction potentials. Under the Environmental Security Technology Certification Program (ESTCP) Project ER21-5152, a field demonstration was conducted at a Navy site on the east coast, and results showed that the technology was highly effective in destroying various PFAS in a liquid concentrate produced from an in situ foam fractionation groundwater treatment system. Another field demonstration was completed at an Air Force base in California, where a treatment train was used to treat PFAS in groundwater. PFAS analytical data and fluoride results demonstrated near-complete destruction of various PFAS. In addition, this demonstration showed: a) high PFAS destruction ratio was achieved in the foam fractionate, even in very high concentration (up to 1,700 mg/L of booster), and b) the effluent was sent back to the influent of the system for further concentration and treatment, resulting in a closed-loop treatment system and no waste discharge.
(Full article...) |
Enviro Wiki Highlights |