Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
| (71 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
{| class="MainPageBG" style="margin: auto; width: 95%; border-spacing:0px;" | {| class="MainPageBG" style="margin: auto; width: 95%; border-spacing:0px;" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width:55%;" |<center><span style="font-size:175%; line-height: 0.2em; vertical-align:top;"><big><span style="color:#008566">Welcome to '''ENVIRO'''</span> <span style="color:#762a87">'''Wiki'''</span></big></span><br /><br /><br /><span style="font-size:150%; color:#008566; line-height: 0.2em; vertical-align:top;"> Peer Reviewed. Accessible. Written By Experts</span></center> |
| − | | style="width: | + | | style="width:40%;" |<center><span style="font-size:110%; vertical-align:top;"> ''Developed and brought to you by '' <br>[[File:MainLogo-serdp-estcp.png|link=https://www.serdp-estcp.org |frameless|center|350px]]</span>''<span style="font-size:140%; vertical-align:top;">Your Environmental Information Gateway</span>'' |
</center> | </center> | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |<span style="line-height: 0.3em;"> The goal of ENVIRO | + | |<span style="width:55%; line-height: 0.3em;"> The goal of ENVIRO Wiki is to make scientific and engineering research results more accessible to environmental professionals, facilitating the permitting, design and implementation of environmental projects. Articles are written and edited by invited experts (see [[Contributors]]) to summarize current knowledge for the target audience on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. </span> |
|<center><span style="font-size:130%"><br />[[#Table of Contents|See Table of Contents]]</span> | |<center><span style="font-size:130%"><br />[[#Table of Contents|See Table of Contents]]</span> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
{| role="presentation" id="mp-upper" style="margin: auto; width: 95%; margin-top:3px; border-spacing: 0px; " | {| role="presentation" id="mp-upper" style="margin: auto; width: 95%; margin-top:3px; border-spacing: 0px; " | ||
<!-- TODAY'S FEATURED ARTICLE --> | <!-- TODAY'S FEATURED ARTICLE --> | ||
| − | | id="mp-left" class="MainPageBG" style="width: | + | | id="mp-left" class="MainPageBG" style="width:55%; padding:0; vertical-align:top; color:#000;" | |
| − | <h2 id="mp-tfa-h2" style="margin:0.5em; background:#cef2e0; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Featured article: | + | <h2 id="mp-tfa-h2" style="margin:0.5em; background:#cef2e0; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"> Featured article: Thermal Conduction Heating for Treatment of PFAS-Impacted Soil</h2> |
| − | <div id="mp-tfa" style="padding:0.0em 1.0em;">[[File: | + | <div id="mp-tfa" style="padding:0.0em 1.0em;">[[File:HeronFig3.png|400px|left|link=Thermal Conduction Heating for Treatment of PFAS-Impacted Soil]]<dailyfeaturedpage></dailyfeaturedpage> |
| − | [[ | + | |
| + | [[PFAS Toxicology and Risk Assessment|(Full article...)]] </div> | ||
| style="border:1px solid transparent;" | | | style="border:1px solid transparent;" | | ||
| Line 31: | Line 32: | ||
<slideshow sequence="random" transition="fade" refresh="7500"> | <slideshow sequence="random" transition="fade" refresh="7500"> | ||
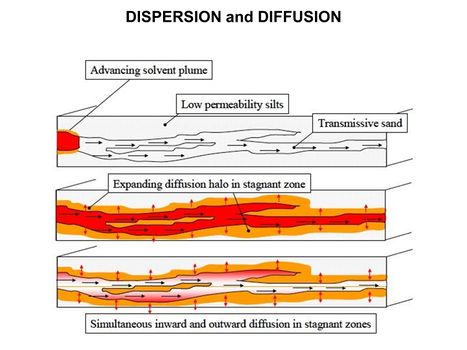
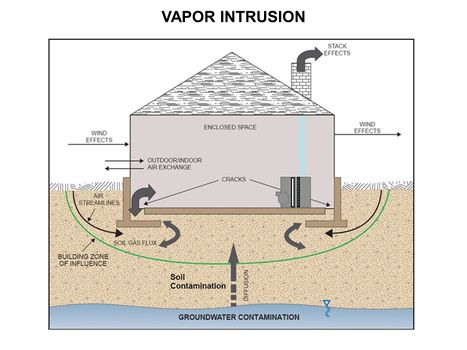
| − | [[File:WH Picture1.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link= | + | [[File:WH Picture1.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Matrix Diffusion|Molecular diffusion slowly transports solutes into clay-rich, lower permeability zones]] |
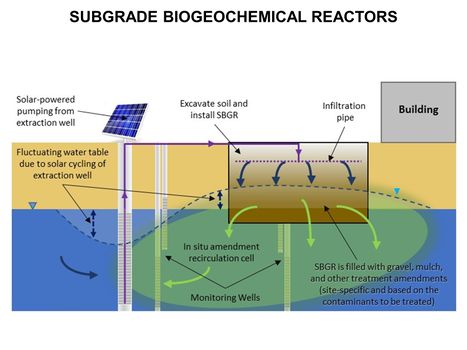
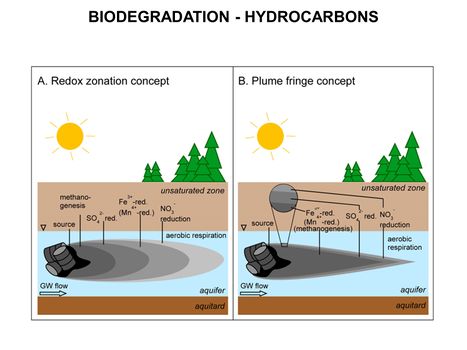
[[File:WH Picture2.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Subgrade Biogeochemical Reactor (SBGR)|Typical subgrade biogeochemical reactor (SBGR) layout. The SBGR is an in situ remediation technology for treatment of contaminated source areas and groundwater plume hot spots<br/>]] | [[File:WH Picture2.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Subgrade Biogeochemical Reactor (SBGR)|Typical subgrade biogeochemical reactor (SBGR) layout. The SBGR is an in situ remediation technology for treatment of contaminated source areas and groundwater plume hot spots<br/>]] | ||
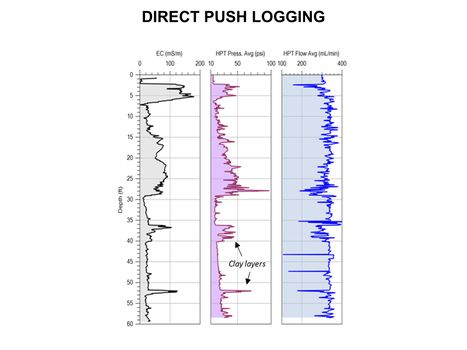
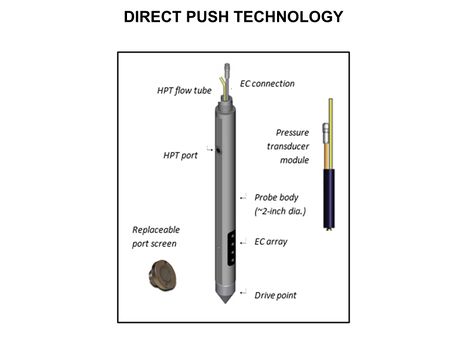
[[File:WH Picture3.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Direct Push Logging|An Hydraulic Profiling Tool (HPT) log with electrical conductivity (EC) on left, injection pressure in middle, and flow rate on the right]] | [[File:WH Picture3.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Direct Push Logging|An Hydraulic Profiling Tool (HPT) log with electrical conductivity (EC) on left, injection pressure in middle, and flow rate on the right]] | ||
| Line 52: | Line 53: | ||
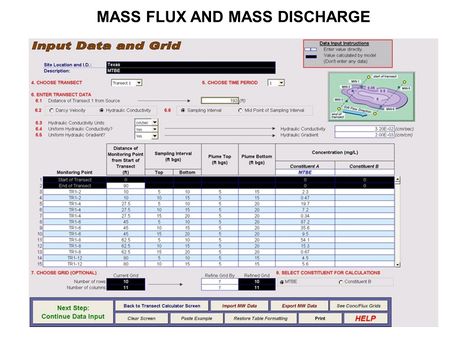
[[File:WH Picture20.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Mass_Flux_and_Mass_Discharge|Data input screen for ESTCP Mass Flux Toolkit]] | [[File:WH Picture20.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Mass_Flux_and_Mass_Discharge|Data input screen for ESTCP Mass Flux Toolkit]] | ||
[[File:WH Picture21.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Bioremediation_-_Anaerobic_Design_Considerations|Amendment addition for biobarrier]] | [[File:WH Picture21.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Bioremediation_-_Anaerobic_Design_Considerations|Amendment addition for biobarrier]] | ||
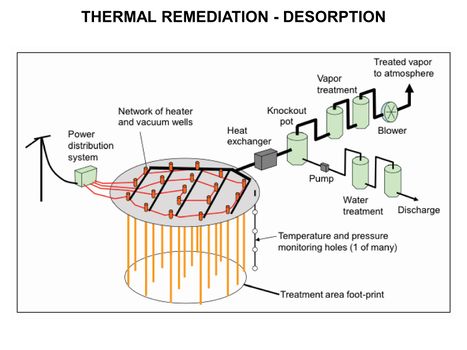
| − | [[File:WH Picture22.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link= | + | [[File:WH Picture22.JPG|thumb|center|x350px|link=Thermal Conduction Heating (TCH)|Thermal Remediation - Desorption schematic]] |
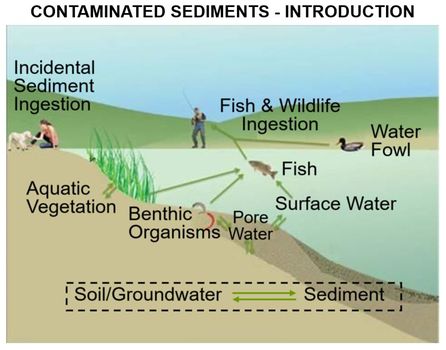
[[File:WH_Picture23.jpg|thumb|center|x350px|link=Contaminated_Sediments_-_Introduction |Key exposure pathways for human health risk from contaminated sediments]] | [[File:WH_Picture23.jpg|thumb|center|x350px|link=Contaminated_Sediments_-_Introduction |Key exposure pathways for human health risk from contaminated sediments]] | ||
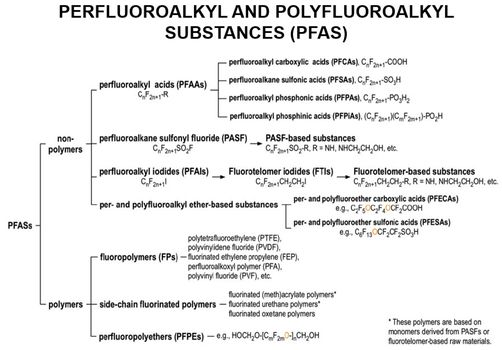
[[File:WH_Picture24.jpg|thumb|center|x350px|link=Perfluoroalkyl_and_Polyfluoroalkyl_Substances_(PFAS)| The PFAS family of compounds]] | [[File:WH_Picture24.jpg|thumb|center|x350px|link=Perfluoroalkyl_and_Polyfluoroalkyl_Substances_(PFAS)| The PFAS family of compounds]] | ||
| Line 79: | Line 80: | ||
*[[Vapor Intrusion (VI)]] | *[[Vapor Intrusion (VI)]] | ||
**[[Vapor Intrusion - Separation Distances from Petroleum Sources]] | **[[Vapor Intrusion - Separation Distances from Petroleum Sources]] | ||
| − | **[[Vapor Intrusion – Sewers and Utility Tunnels as Preferential Pathways]] | + | **[[Vapor Intrusion – Sewers and Utility Tunnels as Preferential Pathways|Vapor Intrusion - Sewers and Utility Tunnels as Preferential Pathways]] |
| + | **[[Assessing Vapor Intrusion (VI) Impacts in Neighborhoods with Groundwater Contaminated by Chlorinated Volatile Organic Chemicals (CVOCs)|Vapor Intrusion - Assessing VI Impacts in Neighborhoods with Groundwater Contaminated CVOCs]] | ||
<u>'''[[Characterization, Assessment & Monitoring]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Characterization, Assessment & Monitoring]]'''</u> | ||
| Line 86: | Line 88: | ||
*[[Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)|Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)]] | *[[Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)|Compound Specific Isotope Analysis (CSIA)]] | ||
*[[Direct Push (DP) Technology]] | *[[Direct Push (DP) Technology]] | ||
| − | **[[Direct Push Logging | | + | **[[Direct Push Logging |Direct Push Logging]] |
| − | **[[Direct Push Sampling | | + | **[[Direct Push Sampling |Direct Push Sampling]] |
*[[Geophysical Methods | Geophysical Methods]] | *[[Geophysical Methods | Geophysical Methods]] | ||
| − | **[[Geophysical Methods - Case Studies | Case Studies]] | + | **[[Geophysical Methods - Case Studies |Case Studies]] |
| + | **[[Hydrogeophysical Methods for Characterization and Monitoring of Groundwater-Surface Water Exchanges]] | ||
*[[Groundwater Sampling - No-Purge/Passive]] | *[[Groundwater Sampling - No-Purge/Passive]] | ||
*[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)|Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)]] | *[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)|Long-Term Monitoring (LTM)]] | ||
| − | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Analysis | LTM Data Analysis]] | + | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Analysis |LTM Data Analysis]] |
| − | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Variability | LTM Data Variability]] | + | **[[Long-Term Monitoring (LTM) - Data Variability |LTM Data Variability]] |
| − | *[[Molecular Biological Tools - MBTs | Molecular Biological Tools (MBTs)]] | + | *[[Molecular Biological Tools - MBTs |Molecular Biological Tools (MBTs)]] |
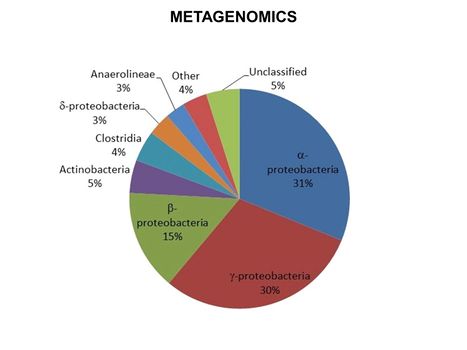
**[[Metagenomics]] | **[[Metagenomics]] | ||
**[[Proteomics and Proteogenomics]] | **[[Proteomics and Proteogenomics]] | ||
**[[Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)]] | **[[Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)]] | ||
**[[Stable Isotope Probing (SIP)]] | **[[Stable Isotope Probing (SIP)]] | ||
| − | *[[Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume - Bemidji Crude Oil Spill | Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume -<br /> Bemidji Crude Oil Spill]] | + | *[[Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume - Bemidji Crude Oil Spill |Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume -<br />Bemidji Crude Oil Spill]] |
| + | *[[OPTically-based In-situ Characterization System (OPTICS)]] | ||
<u>'''[[Climate Change Primer | Climate Change]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Climate Change Primer | Climate Change]]'''</u> | ||
| + | *[[Climate Change Effects on Wildlife]] | ||
*[[Downscaled High Resolution Datasets for Climate Change Projections]] | *[[Downscaled High Resolution Datasets for Climate Change Projections]] | ||
*[[Infrastructure Resilience]] | *[[Infrastructure Resilience]] | ||
| + | *[[Predicting Species Responses to Climate Change with Population Models]] | ||
| + | *[[Restoration of Ecological Function in Terrestrial Systems Impacted by Invasive Species]] | ||
<u>'''[[Coastal and Estuarine Ecology]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Coastal and Estuarine Ecology]]'''</u> | ||
| Line 111: | Line 118: | ||
| style="width:33%; vertical-align:top; " | | | style="width:33%; vertical-align:top; " | | ||
| − | |||
<u>'''[[Contaminated Sediments - Introduction | Contaminated Sediments]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Contaminated Sediments - Introduction | Contaminated Sediments]]'''</u> | ||
| + | *[[Contaminated Sediment Risk Assessment]] | ||
*[[In Situ Treatment of Contaminated Sediments with Activated Carbon]] | *[[In Situ Treatment of Contaminated Sediments with Activated Carbon]] | ||
*[[Mercury in Sediments]] | *[[Mercury in Sediments]] | ||
*[[Passive Sampling of Sediments]] | *[[Passive Sampling of Sediments]] | ||
*[[Sediment Capping]] | *[[Sediment Capping]] | ||
| + | *[[Sediment Porewater Dialysis Passive Samplers for Inorganics (Peepers)]] | ||
<u>'''[[Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids (LNAPLs)]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Light Non-Aqueous Phase Liquids (LNAPLs)]]'''</u> | ||
| Line 127: | Line 135: | ||
<u>'''[[Munitions Constituents]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Munitions Constituents]]'''</u> | ||
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Alkaline Degradation| Alkaline Degradation]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Abiotic Reduction|Abiotic Reduction]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Composting| Composting]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Alkaline Degradation|Alkaline Degradation]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Deposition | Deposition]] | + | **[[Pyrogenic Carbonaceous Matter Enhanced Alkaline Hydrolysis]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Dissolution | Dissolution]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Composting|Composting]] |
| − | *[[ | + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Deposition |Deposition]] |
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Dissolution |Dissolution]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Electrochemical Treatment|Electrochemical Treatment]] | ||
*[[Metal(loid)s - Small Arms Ranges]] | *[[Metal(loid)s - Small Arms Ranges]] | ||
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents – Photolysis | Photolysis]] | + | *[[Passive Sampling of Munitions Constituents|Passive Sampling]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Soil Sampling | Soil Sampling]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents – Photolysis |Photolysis]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - Sorption | Sorption]] | + | *[[Remediation of Stormwater Runoff Contaminated by Munition Constituents |Remediation of Stormwater Runoff ]] |
| − | *[[Munitions Constituents - IM Toxicology | Toxicology]] | + | *[[Munitions Constituents – Sample Extraction and Analytical Techniques|Sample Extraction and Analytical Techniques]] |
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Soil Sampling |Soil Sampling]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - Sorption |Sorption]] | ||
| + | *[[Munitions Constituents - IM Toxicology |Toxicology]] | ||
*[[Munitions Constituents- TREECS™ Fate and Risk Modeling|TREECS™]] | *[[Munitions Constituents- TREECS™ Fate and Risk Modeling|TREECS™]] | ||
| Line 142: | Line 155: | ||
*[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Chlorinated Solvents| MNA of Chlorinated Solvents]] | *[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Chlorinated Solvents| MNA of Chlorinated Solvents]] | ||
| + | *[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Fuels| MNA of Fuels]] | ||
*[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Metal and Metalloids| MNA of Metals and Metalloids]] | *[[Monitored Natural Attenuation (MNA) of Metal and Metalloids| MNA of Metals and Metalloids]] | ||
| − | |||
*[[Natural Source Zone Depletion (NSZD)]] | *[[Natural Source Zone Depletion (NSZD)]] | ||
*[[Monitored Natural Attenuation - Transitioning from Active Remedies| Transitioning from Active Remedies]] | *[[Monitored Natural Attenuation - Transitioning from Active Remedies| Transitioning from Active Remedies]] | ||
<u>'''[[Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)]]'''</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | *[[Hydrothermal Alkaline Treatment (HALT)]] | ||
| + | *[[Lysimeters for Measuring PFAS Concentrations in the Vadose Zone]] | ||
*[[PFAS Ex Situ Water Treatment]] | *[[PFAS Ex Situ Water Treatment]] | ||
| + | **[[PFAS Treatment by Anion Exchange]] | ||
| + | *[[PFAS Monitored Retention (PMR) and PFAS Enhanced Retention (PER)]] | ||
*[[PFAS Soil Remediation Technologies]] | *[[PFAS Soil Remediation Technologies]] | ||
*[[PFAS Sources]] | *[[PFAS Sources]] | ||
| + | *[[PFAS Toxicology and Risk Assessment]] | ||
*[[PFAS Transport and Fate]] | *[[PFAS Transport and Fate]] | ||
| + | *[[PFAS Treatment by Electrical Discharge Plasma]] | ||
| + | *[[Photoactivated Reductive Defluorination - PFAS Destruction | Photoactivated Reductive Defluorination]] | ||
| + | *[[Reverse Osmosis and Nanofiltration Membrane Filtration Systems for PFAS Removal]] | ||
| + | *[[Thermal Conduction Heating for Treatment of PFAS-Impacted Soil]] | ||
| + | *[[Transition of Aqueous Film Forming Foam (AFFF) Fire Suppression Infrastructure Impacted by Per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS)| Transition of Aqueous Film Forming Foam Fire Suppression Infrastructure Impacted by Per and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances]] | ||
| + | | style="width:33%; vertical-align:top; " | | ||
<u>'''[[Regulatory Issues and Site Management]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Regulatory Issues and Site Management]]'''</u> | ||
| Line 162: | Line 187: | ||
*[[Sustainable Remediation]] | *[[Sustainable Remediation]] | ||
| − | + | <u>'''[[Remediation Technologies]]'''</u> | |
*[[Amendment Distribution in Low Conductivity Materials]] | *[[Amendment Distribution in Low Conductivity Materials]] | ||
*[[Bioremediation - Anaerobic|Anaerobic Bioremediation]] | *[[Bioremediation - Anaerobic|Anaerobic Bioremediation]] | ||
| Line 195: | Line 220: | ||
<u>'''[[Soil & Groundwater Contaminants]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Soil & Groundwater Contaminants]]'''</u> | ||
| + | *[[1,2,3-Trichloropropane]] | ||
*[[1,4-Dioxane]] | *[[1,4-Dioxane]] | ||
*[[Chlorinated Solvents]] | *[[Chlorinated Solvents]] | ||
| Line 202: | Line 228: | ||
*[[Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHCs)]] | *[[Petroleum Hydrocarbons (PHCs)]] | ||
*[[Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)]] | *[[Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs)]] | ||
| − | |||
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 14:26, 20 January 2026
Peer Reviewed. Accessible. Written By Experts |
Your Environmental Information Gateway |
| The goal of ENVIRO Wiki is to make scientific and engineering research results more accessible to environmental professionals, facilitating the permitting, design and implementation of environmental projects. Articles are written and edited by invited experts (see Contributors) to summarize current knowledge for the target audience on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. | See Table of Contents |
Featured article: Thermal Conduction Heating for Treatment of PFAS-Impacted SoilRemoval of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from impacted soils is challenging due to the modest volatility and varying properties of PFAS compounds. Thermal treatment technologies have been developed for treatment of semi-volatile compounds such as dioxins, furans, poly-aromatic hydrocarbons and poly-chlorinated biphenyls in soils at temperatures near 325°C. In controlled bench-scale testing, removal of targeted PFAS compounds to concentrations below reporting limits was demonstrated at temperatures of 400°C. Thermal treatment temperatures of at least 400°C and a holding time of 7-10 days are recommended. The energy requirement to treat typical wet soil ranges from 300 to 400 kWh per cubic yard. Extracted vapors have typically been treated using condensation and granular activated charcoal filtration, with thermal and catalytic oxidation as another option which is currently being evaluated for field scale applications.Thermal treatment of PFAS in soils is energy intensive, and the cost of that energy may be prohibitive for some clients. Also, while it often is the least costly option for complete PFAS removal when compared to excavation followed by offsite disposal or destruction, heating soil to treatment temperatures on site or in situ typically takes longer than excavation.
(Full article...)
|
Enviro Wiki Highlights |