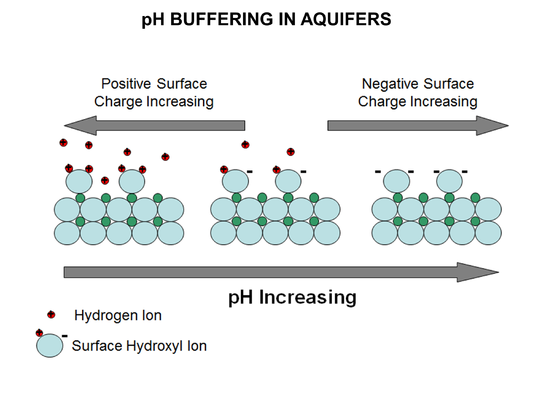
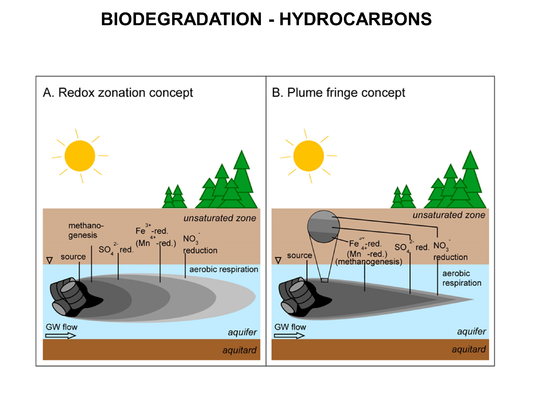
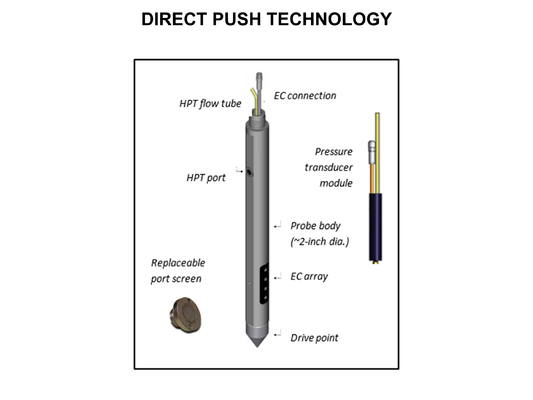
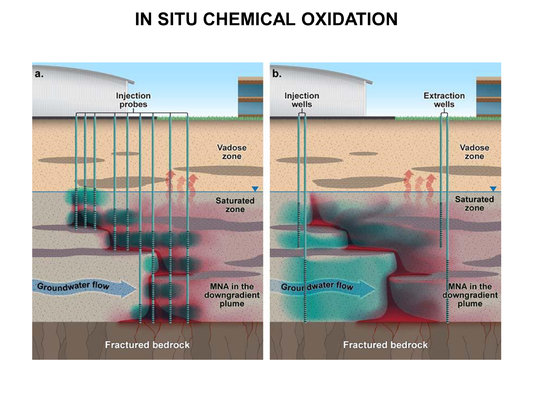
Main Page
| Enviro Wiki aims to be the go-to website for environmental information. US environmental programs such as the Strategic Environmental Research and Development Program (SERDP) and Environmental Security Technology Certification Program (ESTCP) fund cutting-edge environmental research projects. Here, articles written by invited experts (see Contributors) and edited by leaders in this field (see Editors) aim to introduce and summarize current knowledge for environmental project professionals on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. |
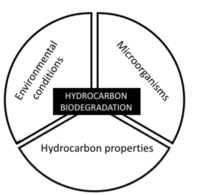
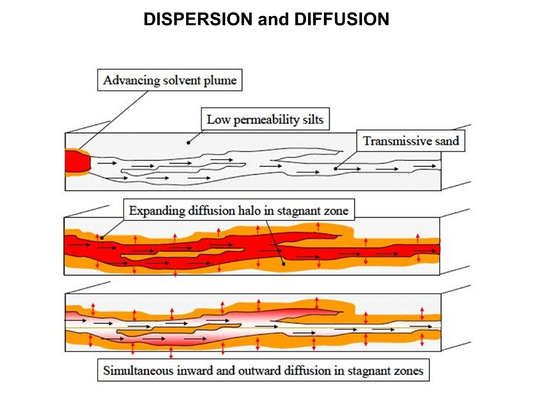
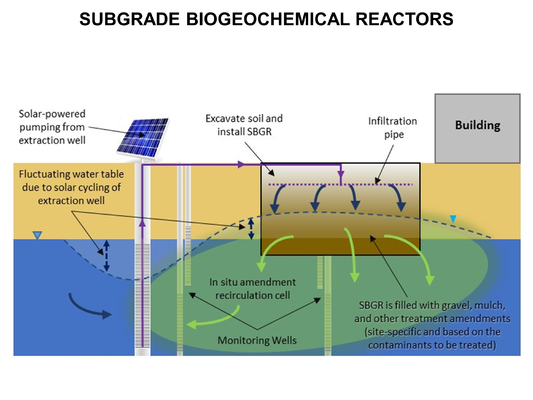
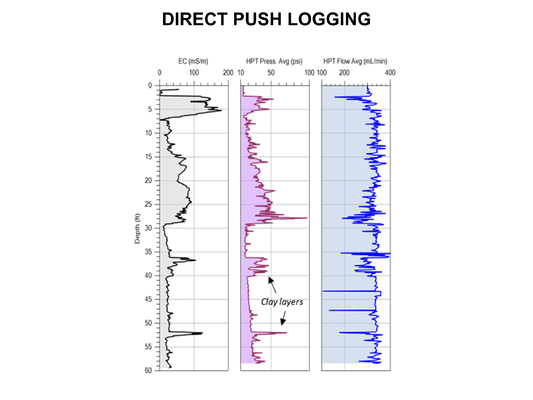
Featured article / Biodegradation - HydrocarbonsThe ultraviolet (UV)/sulfite based reductive defluorination process has emerged as an effective and practical option for generating hydrated electrons (eaq- ) which can destroy per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water. A UV/sulfite treatment system has been demonstrated in two field demonstrations in which it achieved near-complete defluorination and greater than 99% destruction of 40 PFAS analytes measured by EPA method 1633. Hydrated electrons can be produced by photoirradiation of solutes, including sulfite, iodide, dithionite, and ferrocyanide, and have been reported in literature to effectively decompose per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) in water. The hydrated electron is one of the most reactive reducing species, with a standard reduction potential of about −2.9 volts. Though short-lived, hydrated electrons react rapidly with many species having more positive reduction potentials. Under the Environmental Security Technology Certification Program (ESTCP) Project ER21-5152, a field demonstration was conducted at a Navy site on the east coast, and results showed that the technology was highly effective in destroying various PFAS in a liquid concentrate produced from an in situ foam fractionation groundwater treatment system. Another field demonstration was completed at an Air Force base in California, where a treatment train was used to treat PFAS in groundwater. PFAS analytical data and fluoride results demonstrated near-complete destruction of various PFAS. In addition, this demonstration showed: a) high PFAS destruction ratio was achieved in the foam fractionate, even in very high concentration (up to 1,700 mg/L of booster), and b) the effluent was sent back to the influent of the system for further concentration and treatment, resulting in a closed-loop treatment system and no waste discharge.
(Full article...) |
Enviro Wiki Highlights |